Echinococcus multilocularis
FOXES AND OTHER CANIDS
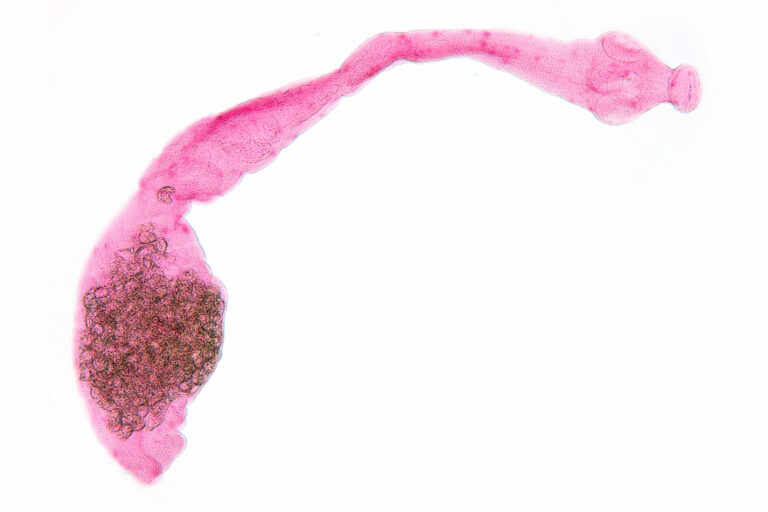
The fox tapeworm Echinococcus multilocularis is a tapeworm widely distributed in Canada, the USA, Europe, and Asia. It parasitizes the small intestine of foxes and other canids and can reach a size of 1.2 – 4.5 mm. This species utilizes various mammals as intermediate hosts, primarily rodents and ungulates, but humans can also become infected as accidental hosts (Craig, 2003).
Human Pathogenicity: Larval stages of the fox tapeworm can invade the tissues and/or organs, causing human alveolar echinococcosis. If left untreated, this can result in severe and potentially fatal liver involvement. Contamination can occur through close contact with an infected definitive host (e.g., dog, cat) or through the ingestion of eggs or larval stages from a contaminated environment or food (Craig, 2003).
-
Craig, P (2003)Echinococcus multilocularis In: Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases, vol. 16, n° 5, p. 437.