Capillaria aerophila
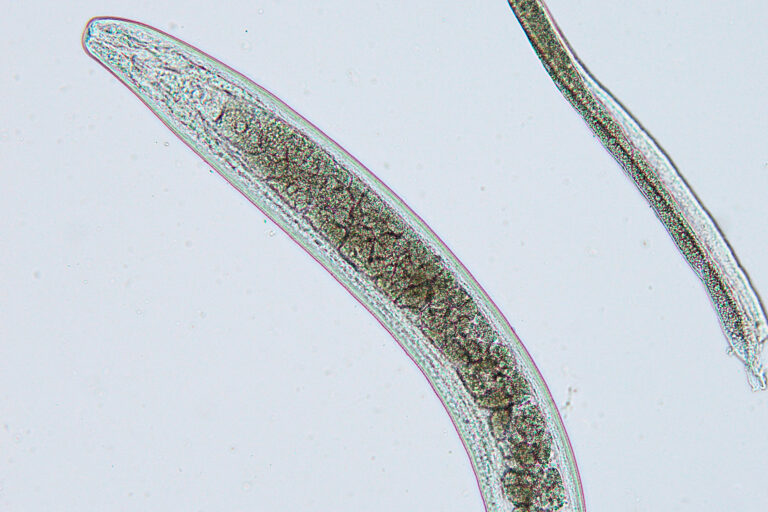
DOGS – CATS – FOXES – MARTENS
The lungworm Capillaria aerophila is a species of nematode that has a hair-like, very narrow body structure (Beck, 2007). The earthworm primarily serves as an intermediate host. Definitive hosts can become infected either by consuming infected earthworms or directly through infectious stages of the lungworm present in the environment. Adult parasites live and reproduce in the epithelium of the trachea and bronchi, causing chronic bronchitis that leads to inflammation, sneezing, wheezing, and dry cough. The eggs are coughed up, swallowed, and expelled through the feces (Traversa et al., 2011).
Human Pathogenicity: Humans can also become infected by ingesting infectious stages of the lungworm. Infection can result in coughing, fever, shortness of breath, and bronchitis (Aftandelians et al., 1977; Lalošević et al., 2008).
-
Aftandelians, R et al. (1977)Pulmonary capillariasis in a child in Iran. In: The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene, vol. 26, n° 1, p. 64–71.
-
Beck, W (2007)Endoparasiten beim Igel. In: Wiener klinische Wochenschrift, vol. 119, n° 19-20 Suppl 3, p. 40–44.
-
Lalošević, D et al. (2008)Pulmonary Capillariasis Miming Bronchial Carcinoma. In: The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene, vol. 78, n° 1, p. 14–16.
-
Traversa, D et al. (2011)New insights into morphological and biological features of Capillaria aerophila (Trichocephalida, Trichuridae). In: Parasitology Research, 109 Suppl 1, S97-104.