Euryhelmis squamula
MAMMALS
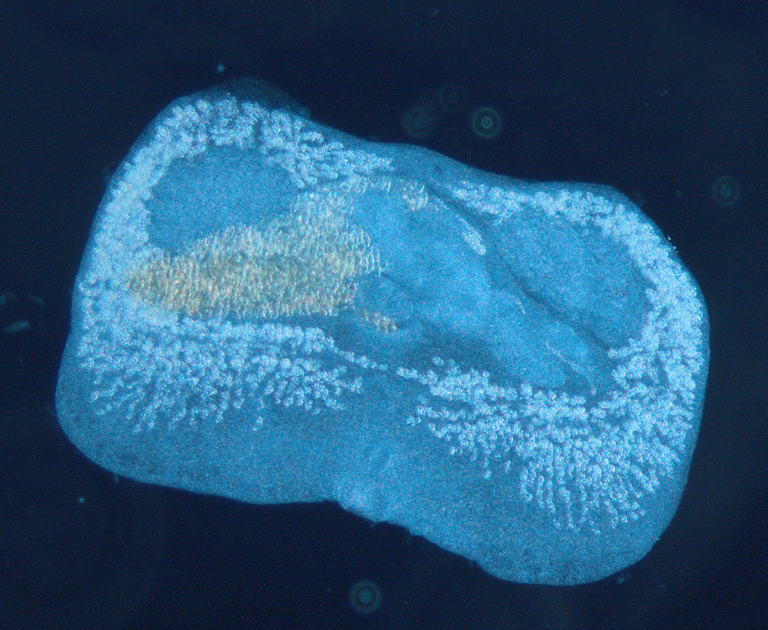
The characteristic body structure of digeneans is bilaterally symmetrical and usually dorsoventrally flattened (Deplazes et al., 2021), in the case of Euryhelmis squamula the body is wider than long (Kim et al., 2021). The life cycle of E. squamula is not yet fully known, but like most parasitic worms, this species requires two intermediate hosts during its development. The first intermediate hosts of this parasite species are snails of the Hydrobiidae family, the second intermediate hosts are amphibians such as the grass frog Rana temporaria (Anderson and Pratt, 1965). Infection occurs via the ingestion of infected intermediate hosts.
Human pathogenicity: There is no known infestation of humans with Euryhelmis squamula.
Deplazes, P., Joachim, A., Mathis, A., Strube, C., Taubert, A., Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. von, Zahner, H. (2021) Parasitologie für die Tiermedizin, 4., überarbeitete Auflage. ed. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart New York
Kim, H.C., Hong, E.J., Ryu, S.Y., Park, J., Cho, J.G., Yu, D.H., Chae, J.S., Choi, K.S., Park, B.K. (2021) Euryhelmis squamula (Digenea: Heterophyidae) Recovered from Korean Raccoon Dog, Nyctereutes procyonoides koreensis, in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 59, 303–309. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.3.303
-
Anderson, G.A., Pratt, I. (1965)Cercaria and first intermediate host of Euryhelmis squamula. The Journal of Parasitology 13–15
-
Deplazes, P et al. (2021)Parasitologie für die Tiermedizin, 4., überarbeitete Auflage. ed. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart New York
-
Kim, H.C., Hong et al. (2021)Euryhelmis squamula (Digenea: Heterophyidae) Recovered from Korean Raccoon Dog, Nyctereutes procyonoides koreensis, in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 59, 303–309. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.3.303